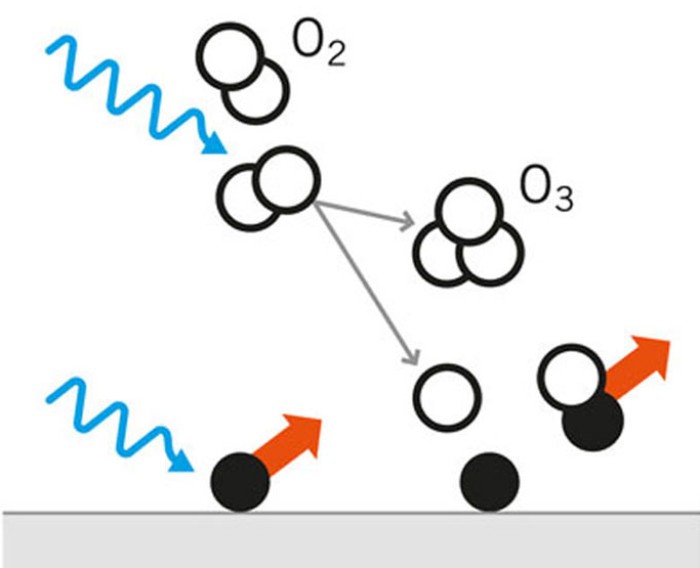
High-energy UV photons break up contaminants by means of photo-decomposition and separate them into environmentally friendly components.
For example, vacuum UV radiation with a wavelength of 185 nm decomposes long-chain molecules by means of direct photolysis.
The process can be accelerated by adding oxidizing agents such as ozone (O3) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Contaminants in water and air are converted into harmless molecules.